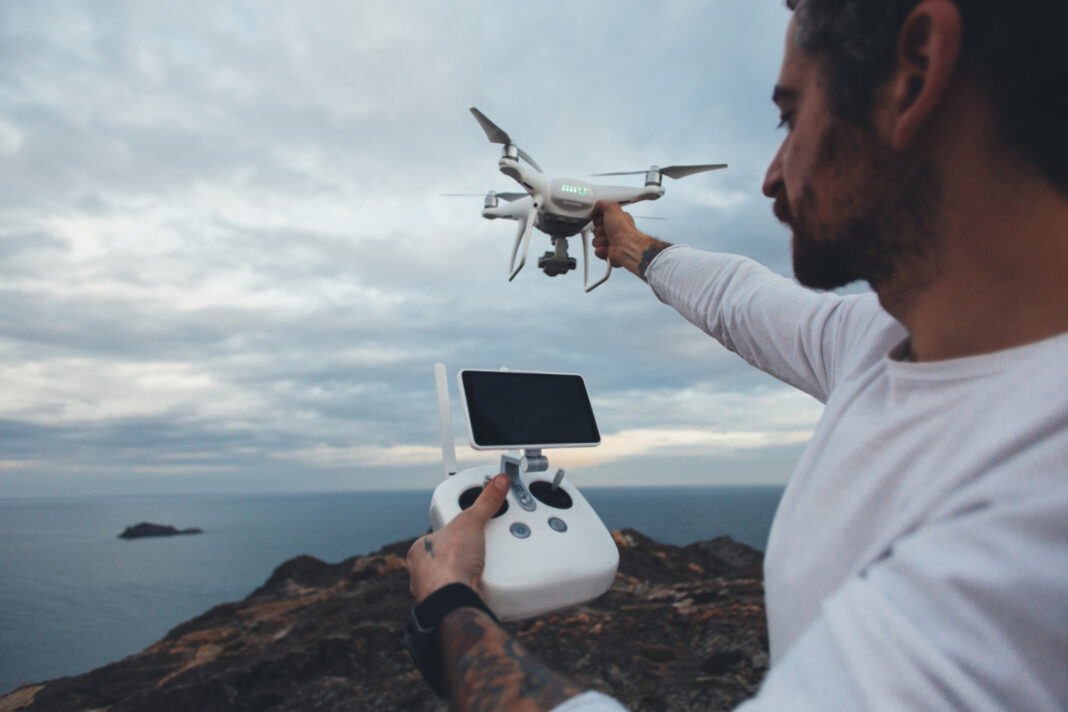
Drones, once exclusive to military operations, have become an indispensable tool across industries and an exciting hobby for enthusiasts. From revolutionizing photography to enhancing logistics and disaster management, these unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) have transformed the way we perceive and interact with technology. This blog explores the current trends, applications, and the future of drones, optimized for maximum SEO visibility.
The Rise of Drones: A Brief History
The concept of drones dates back to the early 20th century, primarily for military reconnaissance. However, it wasn’t until the 21st century that drones became accessible to the public, thanks to advancements in technology and decreasing production costs. The integration of GPS, high-resolution cameras, and smart sensors has propelled drones into mainstream use.
Current Trends in the Drone Industry
- Consumer Drones for Photography and Videography Drones equipped with 4K cameras and gimbal stabilization have redefined creative storytelling. Platforms like DJI, Autel Robotics, and Parrot lead the market with versatile options for amateurs and professionals.
- Drones in Delivery Services Companies like Amazon and UPS are testing drone deliveries to enhance logistics efficiency. These UAVs promise to reduce delivery times and costs, particularly in remote areas.
- Agricultural Drones Smart drones are transforming agriculture by providing aerial views of crop health, irrigation levels, and pest infestations. This data enables precision farming, improving yields and sustainability.
- Inspection and Maintenance Industries like energy and construction use drones for inspecting pipelines, power lines, and infrastructure. These UAVs can access hard-to-reach areas, reducing risks for human workers.
- Emergency Response and Disaster Management Drones play a crucial role in search and rescue operations, mapping disaster-stricken areas, and delivering medical supplies to inaccessible locations.
Benefits of Drone Technology
- Cost Efficiency: Drones reduce the need for expensive equipment and manpower.
- Environmental Monitoring: UAVs are used for tracking wildlife, studying ecosystems, and monitoring deforestation.
- Improved Safety: Drones can perform dangerous tasks, minimizing risks to human life.
The Regulatory Landscape
As drone usage grows, so does the need for regulations. Authorities worldwide, such as the FAA in the United States, have implemented guidelines for safe drone operation. These include restrictions on flight zones, maximum altitudes, and mandatory registration for certain types of UAVs.
To avoid legal complications, operators should:
- Stay updated on local drone laws.
- Use geofencing technology to avoid restricted areas.
- Obtain necessary certifications for commercial use.
The Future of Drones
- Advanced Autonomy With AI integration, future drones will feature enhanced autonomy, enabling them to navigate complex environments without human intervention.
- Swarm Technology Inspired by nature, swarm drones will collaborate to perform tasks like surveillance, search and rescue, and large-scale data collection.
- Urban Air Mobility (UAM) Drones will pave the way for flying taxis and other urban air transportation systems, addressing traffic congestion in metropolitan areas.
- Sustainable Innovations Electric-powered drones and solar charging solutions will make UAVs more environmentally friendly.