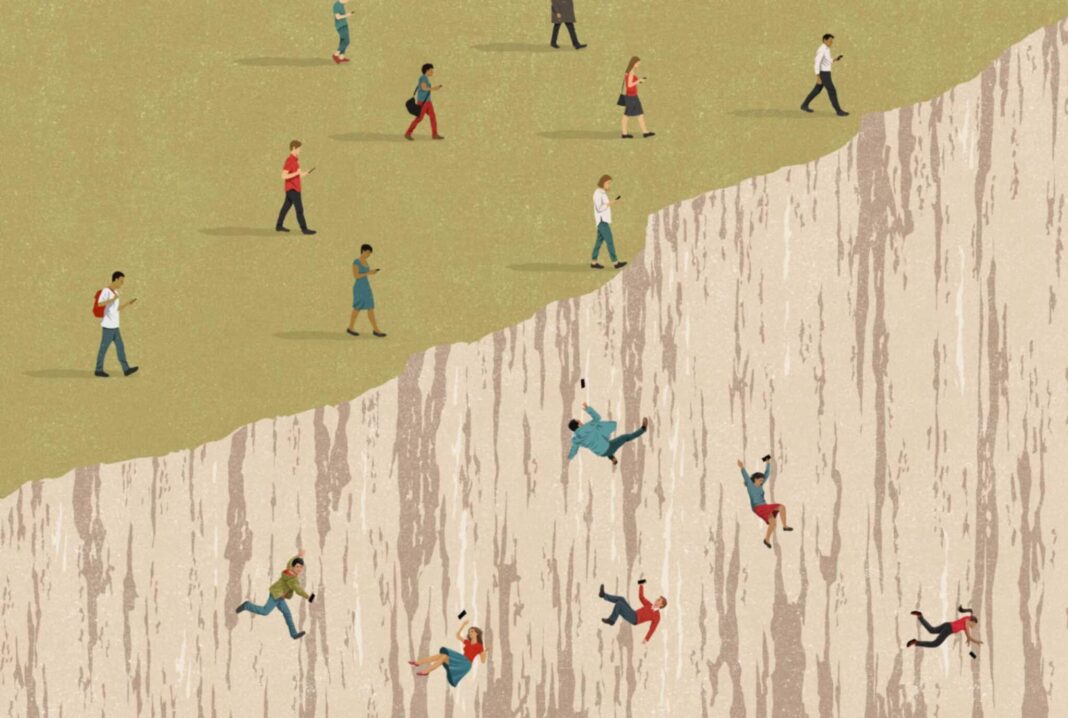
Why Are People So Addicted to Their Phones? Exploring the Psychological, Social, and Technological Reasons Behind Smartphone Dependence
In today’s digital world, phone addiction has become a common issue, affecting people of all ages. Smartphones serve as our gateway to information, entertainment, social interaction, and more, making it hard for many to put them down. But why exactly are we so hooked? Let’s dive into the psychological, social, and technological reasons behind smartphone dependence and examine how this addiction affects our mental health, productivity, and relationships.

1. Instant Gratification and Dopamine Release
One of the main psychological reasons behind phone addiction is the instant gratification that smartphones provide. Whether it’s checking a new message, scrolling through social media, or refreshing news feeds, each action delivers immediate rewards in the form of new information, social connections, or entertainment. This cycle of instant rewards releases dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward, in our brains. Over time, we start to crave that dopamine release, making us reach for our phones repeatedly to experience the same gratification.
2. Social Validation and Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)
Social media plays a major role in keeping us glued to our phones. Platforms like Instagram, Facebook, and Twitter are designed to capture attention and encourage frequent engagement. Each like, comment, or share acts as a form of social validation, making users feel valued and connected. The desire for approval from others can create a habit loop, where people post, wait for responses, and check their notifications continuously. Additionally, the fear of missing out (FOMO) drives people to stay updated on social media to avoid feeling left out. FOMO can create a sense of anxiety, compelling individuals to check their phones frequently for any updates or news, further fueling addiction.
3. Endless Information and Entertainment
Smartphones provide unlimited access to information and entertainment. With a single tap, users can browse articles, watch videos, play games, and more. The availability of such diverse content leads to endless scrolling, where users lose track of time as they dive into a loop of never-ending information. This phenomenon, known as the “infinite scroll,” is a design tactic used by social media platforms and news websites to keep users engaged for extended periods. The constant availability of new content keeps the brain stimulated, making it difficult to put the phone down.
4. The Role of Habit Formation and Conditioning
Smartphones encourage habit formation through constant notifications and alerts. Over time, users become conditioned to check their phones in response to certain triggers, such as the sound of a notification or the sight of their phone screen lighting up. This habit formation is often subconscious; people may pick up their phones out of habit rather than a genuine need to check something. These habits can become deeply ingrained, making it challenging to resist the urge to reach for the phone, even during inappropriate times, like during meetings or while spending time with loved ones.
5. Convenience and Dependence on Digital Tools
Smartphones are multifunctional devices that offer a wide array of tools and services, from GPS navigation and online shopping to work emails and personal calendars. As people increasingly rely on their phones to manage different aspects of their lives, they develop a dependency on these devices. The convenience that smartphones offer makes them indispensable, further reinforcing the habit of checking and using the phone throughout the day. This dependence on digital tools can make people feel “lost” or “incomplete” without their phones, contributing to addictive behavior.
6. Escapism and Stress Relief
For many, smartphones serve as an escape from reality. People often use their phones to relieve stress, distract themselves from negative emotions, or avoid dealing with real-life challenges. Whether it’s scrolling through Instagram to unwind, playing mobile games to pass the time, or watching funny videos to lift their mood, phones provide an easy escape from daily stressors. While this can be helpful in moderation, excessive reliance on phones for escapism can prevent people from addressing the root causes of their stress, leading to a cycle of avoidance and dependence.
The Impact of Phone Addiction on Mental Health and Relationships
While smartphones offer numerous benefits, excessive use can take a toll on mental health and relationships. Studies have shown that prolonged screen time and social media use can lead to increased anxiety, depression, and feelings of loneliness. The constant need for validation and comparison on social media can erode self-esteem, while the habit of checking phones during social interactions can strain personal relationships. People often struggle to be fully present in face-to-face conversations, leading to feelings of disconnection and isolation among family and friends.
How to Manage Phone Addiction and Reclaim Control
Breaking free from phone addiction requires conscious effort and self-discipline. Simple strategies, like setting daily screen time limits, turning off non-essential notifications, and designating “phone-free” times, can help reduce phone usage. Mindfulness practices, such as focusing on in-person interactions and being present in the moment, can also alleviate the urge to check the phone constantly. By taking small steps, individuals can regain control over their phone habits and enjoy a healthier, more balanced relationship with technology.
FAQs:
1. What is phone addiction?
Phone addiction, often referred to as “nomophobia” (the fear of being without a mobile phone), is a behavioral addiction that leads people to excessively use their smartphones. It involves a compulsive urge to check and use the phone frequently, even when it interferes with daily life, work, or personal relationships.
2. Why are people so addicted to their phones?
People become addicted to their phones for various reasons, including instant gratification, social validation, the fear of missing out (FOMO), and the endless supply of information and entertainment. Psychological factors like dopamine release and habit formation also play a role, as well as social factors such as the desire for approval on social media.
3. What are the signs of phone addiction?
Signs of phone addiction include constantly checking your phone, using it as a way to relieve stress or escape reality, feeling anxious without it, prioritizing phone use over in-person interactions, and finding it difficult to stop using it even during important events or tasks.
4. How does phone addiction affect mental health?
Excessive phone use, especially on social media, has been linked to anxiety, depression, low self-esteem, and loneliness. The constant need for social validation and comparison can lead to negative self-image, while the dopamine-driven habit of frequent checking can increase anxiety levels.
5. Can phone addiction impact relationships?
Yes, phone addiction can strain relationships by reducing quality time and personal connection. Being constantly distracted by a phone during conversations can make people feel unimportant or ignored, leading to feelings of disconnection and resentment in relationships.
6. What causes the fear of missing out (FOMO) on social media?
FOMO is triggered by the constant exposure to other people’s highlight reels on social media, making users feel as if they’re missing out on experiences, events, or achievements. This fear drives people to stay connected and check their phones frequently to avoid feeling left out.
7. How does phone addiction develop over time?
Phone addiction develops through a cycle of habit formation, where frequent phone use becomes a response to triggers like notifications, boredom, or stress. Over time, this habit becomes reinforced by dopamine release and social validation, making it hard to break.
8. What is “infinite scroll,” and why is it addictive?
Infinite scroll is a design feature used by social media and content apps that allows users to keep scrolling endlessly without reaching an endpoint. This design creates a loop of continuous engagement, keeping users hooked for longer periods and making it hard to stop.
9. Are certain apps more addictive than others?
Yes, some apps are designed with features that encourage habitual use, such as social media apps with likes, comments, and notifications. These features are intended to stimulate dopamine release and reinforce the habit loop, making users feel compelled to check and engage frequently.
10. How can I break free from phone addiction?
Breaking phone addiction requires setting boundaries and being intentional with phone usage. You can set screen time limits, turn off non-essential notifications, designate “phone-free” periods, and engage in hobbies or activities that don’t involve your phone. Practicing mindfulness and focusing on in-person interactions can also help reduce dependence.
11. Is phone addiction a real addiction?
While phone addiction may not involve physical substances like drugs or alcohol, it is considered a behavioral addiction, as it involves compulsive behavior with negative effects on mental health and well-being. Behavioral addictions like phone addiction can have serious consequences and may require intervention.
12. Can phone addiction lead to physical health issues?
Yes, excessive phone use can lead to physical health issues such as eye strain, poor posture, neck pain (often called “text neck”), and sleep disturbances due to blue light exposure before bed. These issues can worsen over time with prolonged phone use.
13. Why is dopamine important in understanding phone addiction?
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter linked to pleasure and reward. Every time we check our phones and see something enjoyable or validating, such as a new message or notification, dopamine is released in our brains, reinforcing the habit. This cycle of reward-driven behavior is a key factor in developing and maintaining phone addiction.
14. How does phone addiction affect sleep?
Phone addiction often leads to excessive screen time before bed, which exposes users to blue light that can interfere with melatonin production. This disrupts the sleep-wake cycle, making it harder to fall asleep and reducing the quality of sleep, leading to fatigue and other health issues.
15. Can children and teenagers become addicted to phones?
Yes, children and teenagers are particularly vulnerable to phone addiction due to the formative stage of their social and cognitive development. Social media, online games, and peer pressure can create habits and dependencies that are hard to break, impacting their mental health, academic performance, and social skills.